BEEZ INDUSTRIES MOROCCO
The world is on the cusp of a technological revolution that promises to
fundamentally transform industries, economies, and societies. It's called
Industry 4.0, and it represents the fusion of the physical, digital, and
biological worlds in a way that will impact all disciplines, industries, and
economies.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, builds on
the legacy of previous industrial revolutions. The First Industrial Revolution
saw the mechanization of production through water and steam power, followed by
the Second Industrial Revolution that brought about mass production through
electricity and assembly lines. The Third Industrial Revolution introduced
automation, electronics, and information technology. Now, we are entering the
Fourth Industrial Revolution, where cyber-physical systems, the Internet of
Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data are taking center
stage.
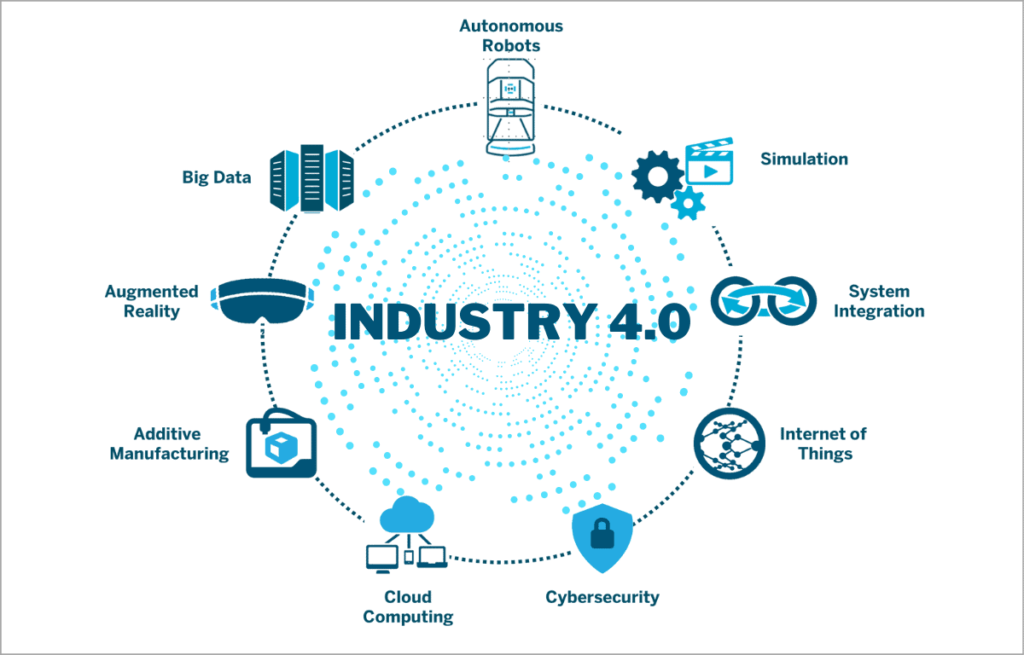
Key Pillars of Industry 4.0
IoT and Connectivity: In Industry 4.0, devices and machines are equipped
with sensors and connected to the internet. This enables real-time data
exchange, monitoring, and control, creating smart factories and supply chains.
Big Data and Analytics: The sheer volume of data generated by IoT
devices is immense. Big data analytics and machine learning allow us to derive
valuable insights from this data, leading to improved decision-making,
predictive maintenance, and increased efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI is at the heart of
Industry 4.0. It's used for predictive analysis, quality control, and
automation. AI-driven robots and autonomous systems are increasingly being used
in manufacturing processes.
Automation and Robotics: Advanced robotics and automation technologies
are being integrated into production lines. These robots can work alongside
humans, performing tasks with precision and speed.
3D Printing: Additive manufacturing or 3D printing is revolutionizing
prototyping and customization. It allows for rapid, cost-effective production
of complex parts.
Cloud Computing: The cloud is the backbone of Industry 4.0. It enables
remote access to data, software, and processing power, making it easier for
companies to scale and adopt new technologies.
Impact on Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is reshaping manufacturing in profound ways:
Smart Factories: Factories are becoming smarter, with machines that
communicate with each other. This enables adaptive and flexible manufacturing
processes.
Predictive Maintenance: Equipment and machinery can predict when they
will need maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
Customization: Mass production is giving way to mass customization.
Products can be tailored to individual customer needs.
Sustainability: Industry 4.0 can help reduce waste and energy
consumption, making manufacturing more sustainable.
Beyond Manufacturing
Industry 4.0's impact goes well beyond manufacturing:
Supply Chain Management: Improved visibility and control over the supply
chain enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
Healthcare: Telemedicine, wearable devices, and AI-driven diagnostics
are transforming healthcare delivery.
Smart Cities: IoT and data analytics can improve traffic management,
energy use, and public services.
Education: Personalized learning and online education are becoming more
effective with AI.
Energy: Smart grids and IoT help optimize energy distribution and
consumption.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Industry 4.0 presents immense opportunities, it also poses
challenges. Concerns about data security, privacy, and the impact on employment
need to be addressed. Companies and governments must adapt to stay competitive.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 is ushering in a new era of innovation and
productivity. It's changing the way we manufacture, work, and live. Embracing
this revolution and managing its challenges is key to a prosperous and
sustainable future. Industry 4.0 is not just the future; it's the present, and
it's here to stay.



0 Commentaires